 Chocolate is everyone’s favorite. It is a hard core sweet. There is chocolate candy, pudding, cake, and pie. And don’t forget chocolate fudge, brownies, and doughnuts. Yet it must be asked, has the average person even heard of the chocolate alkaloid theobromine?
Chocolate is everyone’s favorite. It is a hard core sweet. There is chocolate candy, pudding, cake, and pie. And don’t forget chocolate fudge, brownies, and doughnuts. Yet it must be asked, has the average person even heard of the chocolate alkaloid theobromine?
Coffee
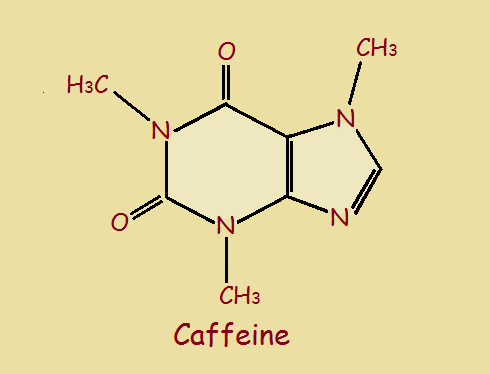
Chocolate is not our only “favorite” food. We have bacon. We have beer. We have coffee. We have pizza. Just as coffee contains an alkaloid caffeine, there is a chocolate alkaloid theobromine.
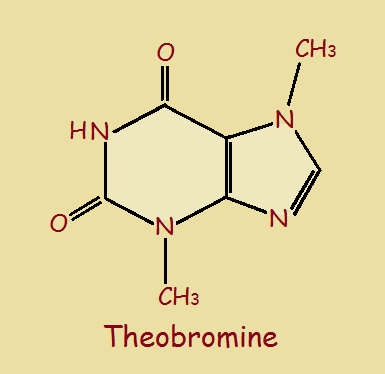
 Structure of Theobromine?
Structure of Theobromine?
An alkaloid is a natural occurring, nitrogen containing base. Alkaloids produce physiological effects. These are sometimes good, sometimes bad. Theobromine is a xanthine alkaloid. Caffeine is a xanthine alkaloid. There is little difference between the two. In fact, there is only one methyl group difference (‒CH3)!
Compare the images.
Theobromine has the basic chemical formula C7H8N4O2. Its twenty one atoms include seven carbon, eight hydrogen, four nitrogen, and two oxygen atoms.
What is the Physiological Action of Theobromine?
As to physiological action, the chocolate alkaloid theobromine reduces blood pressure. It increases urination. Despite chocolate’s use in sweets, theobromine fights tooth decay.
Even though there are benefits to humans eating theobromine, some animals are adversely affected. Even fatally so.
In Conclusion – The Chocolate Alkaloid Theobromine

The viewpoint concerning human consumption of chocolate has gone through a number of changes. During the 3rd quarter of the 20th century, it was considered ill advised to eat the treat. A few decades later this notion changed. Chocolate is now considered a most healthful food.
Note: You might also enjoy Chlorogenic Acid and Its Derivatives in Coffee
References:
- Decoded Science: The Manufacture and Chemistry of Chocolate
- Quintessence Publishing: Evaluation of Human Enamel Surfaces Treated with Theobromine: A Pilot Study
- The Merck Veterinary Manual: Chocolate
